“Mom never should have gotten the pacemaker,” the daughter said to me. We were sitting at the bedside of the old lady who seemed like it was going to take forever for her to die. Not that anyone involved in this case wanted to hasten death, just not prolong the process.
I asked her about the history of her mother’s pacemaker. “Was there a benefit to her when it was first implanted?”
“Oh yes,” she said. “Her quality of life improved greatly.”
There you go. Treatments are begun at a time when they offer clear benefit to the patient. Sometimes they provide years of benefits.
I have seen this dilemma over and over again. A patient begins a treatment at a time when they are competent and they choose to use a device or medication. Then they get to their last days or weeks and can no longer enter into a discussion about a treatment. So families occasionally feel they are going against the patient’s wishes if they withdraw the treatment.
Increasingly, hospice workers are finding patients with defibrillators surgically implanted in their chests. For patients with a particular type of abnormality, these devices provide a jolt of electricity to the heart if it is out of rhythm. They are a smaller version of what you see on television shows where a rescue squad or an emergency room staff applies the “paddles” to a patient and shocks their heart back to life. There is no question that the implanted devices benefit many patients.
But what if someone is dying?
But what if someone is dying of cancer, respiratory failure or advanced Alzheimer’s disease? The family and medical team know the end is near…perhaps within hours or days at most. The goal now is a peaceful death rather than prolonging a life. So the heart finally gives out only to be shocked back to life. Often the decision is made to turn off the defibrillator.
But wait! Didn’t the patient make the choice to have the device implanted? Are not the family members going against the competent choice of the patient? Technically, they are changing the treatment plan adopted by the patient. But that plan was developed under a vastly different set of circumstances. At the time, perhaps the patient’s only significant medical problem was an irregular heartbeat in need of an occasional shock.
The new information may be that food and fluid intake has ended, the kidneys are shutting down, and the patient has been unconscious for days. It would have been nice to have had a conversation with a patient when they had the capacity about the conditions where they would have wanted the defibrillator turned off. What if a doc had said, “Your disease is advancing. In the end, you may be unconscious for days and not be able to interact with your family. If your heart stops, the device in your chest may shock it back to life. We could turn it off and allow a peaceful death to occur. What would you want us to do if there is no hope of your recovery?”
Rarely, do such conversations happen.
“Under what conditions would you want your ventilator turned off?”
While I was a nursing home chaplain I had the privilege of working with a young man in his 20s who had muscular dystrophy. Bill breathed with the assistance of a ventilator that forced air into his lungs through a hole in his throat. He wanted to do a “living will.” He wanted to assign someone to make medical decisions for him if he lost mental capacity and he wanted to put in writing that he did not want to be hooked up to machines artificially prolonging his life if he were terminally ill. One of the volunteers who visited Bill on a regular basis was a lawyer and he drew up the documents for the patient to “sign.”
Bill was unable to use his hand to sign the piece of paper. He was to give verbal assent to the document in front of witnesses. So before the lawyer, another nursing home staff member, and myself he told us what his wishes were. I signed as a witness to his choices. I was curious. He said he did not want to be hooked up to machines if he was dying. But he obviously was choosing to be on the breathing machine now.
I asked, “Under what conditions would you want your ventilator turned off?” Bill looked to his roommate and said, “If I get like John.”
John was also in his early 20s and had been in a non-responsive condition for several years. A football injury damaged his spinal cord and left him where he could breathe on his own but had no purposeful interaction with the world around him. He received food and fluids through a feeding tube.
Now we knew. Bill was actually transferred to a group home for similarly affected young people and died there a few years later. I do not know if the ventilator was ever turned off.
In the very last days of life the “routine” may become “heroic”
There are many medical interventions that may be considered “routine” under normal circumstances. Pacemakers, blood pressure medicine, and antibiotics to cure pneumonia are just a few that come to mind. But when a patient is in the very last days of life the “routine” may become “heroic” in that the interventions may prolong the life of the patient. Families may choose to withdraw or withhold such treatments in the hope of providing a more peaceful death.
To withdraw is not going against the patient’s wishes. The family is acting as the patient’s agent on the new information that the patient is in the last days of life. Now the goal is to provide for a comfortable death and not to prolong the dying process.
Photo by Steven HWG on Unsplash
 Jill McClennen asked me to come back on her “Seeing Death Clearly” podcast. This time the topic was “End-of-Life Nutrition & Hydration.” We covered feeding tubes as they relate to swallowing difficulties following a stroke, cancer, or dementia. We also talked about the normal loss of appetite in the dying patient. We spent some time discussing “voluntarily stopping eating and drinking” (VSED) both for the competent patient and by advance directive for the dementia patient.
Jill McClennen asked me to come back on her “Seeing Death Clearly” podcast. This time the topic was “End-of-Life Nutrition & Hydration.” We covered feeding tubes as they relate to swallowing difficulties following a stroke, cancer, or dementia. We also talked about the normal loss of appetite in the dying patient. We spent some time discussing “voluntarily stopping eating and drinking” (VSED) both for the competent patient and by advance directive for the dementia patient.
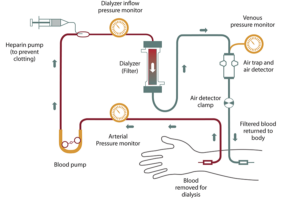


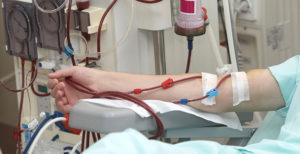 In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation published clinical practice guidelines on the evaluation, classification, and stratification of chronic kidney disease (CKD). These guidelines were based on levels found in a patient’s blood chemistry. Patients are classified as “normal/mild,” “moderate,” or “severe.” Those with more severe conditions may be put on dialysis.
In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation published clinical practice guidelines on the evaluation, classification, and stratification of chronic kidney disease (CKD). These guidelines were based on levels found in a patient’s blood chemistry. Patients are classified as “normal/mild,” “moderate,” or “severe.” Those with more severe conditions may be put on dialysis. In 2017,
In 2017, 
